Costa Rica
Renewable energy cooperatives
"I am a smallholder organic coffee producer and until a few years ago, there were major concern in the area among producers. We were aware that we were doing things in the wrong way, that we were contaminating and destroying the environment. And this led us to get organised in a group of small-scale producers. Coopesantos is a cooperative that I appreciate very much because it’s ours and has managed to reach even the most remote corner in the region"
Manuel Corrales – Member of Coopesantos R.L.
Renewable energy cooperatives in Costa Rica
Location: Costa Rica
Year of Foundation: 1965 and 1972
Number of Members: around 200,000
Sector: Electric cooperatives
Key themes: Renewable energy, climate action, community development
- 7 Affordable and clean energy
- 11 Sustainable cities and communities
- 13 Climate action
- 15 Life on land
Coop Story
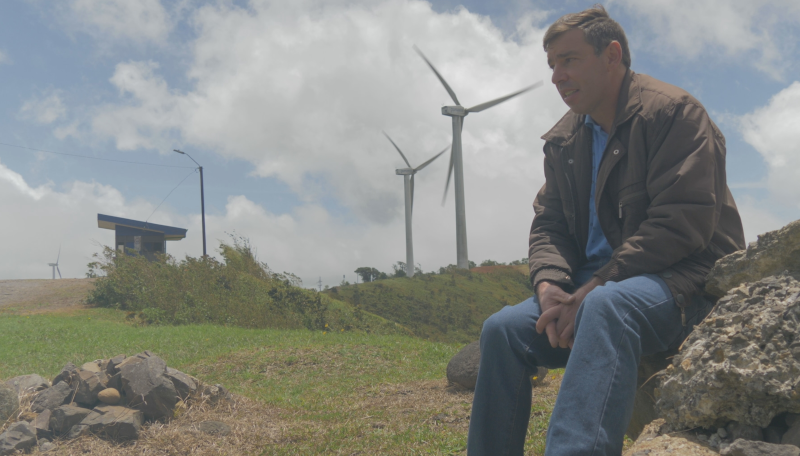
In Costa Rica there are four electricity cooperatives, namely Coopelesca, Coopeguanacaste, Coopesantos - the three of them founded in 1965 - and Coopealfaroruiz, founded in 1972. All together, they form the Conelectrica Consortium and gather around 200,000 members.
Initially, these cooperatives were created to meet rural communities’ need to access electricity in remote areas. Nowadays, these cooperatives have three main functions: to produce electricity from renewable sources (hydropower; solar and wind); to distribute electricity to every single remote corner of the country; and to reinvest profit in their own communities by supporting sustainable development projects.

Key Learning Points
- Investing in a diversified matrix of renewable energy is a key strategy to cope with climate change and at the same time reduce dependency on hydrocarbons. Cooperatives are key actors in this regard.
- The difference between the multinational energy provider and the coop is that the latter reaches even the most remote households and reinvests its profit in local development.
- Renewable energy coops can be a means to raise awareness about environmental conservation and sustainable development, as coops, beyond producing and distributing energy, provide trainings and engage with communities in collective action in defense of natural resources.